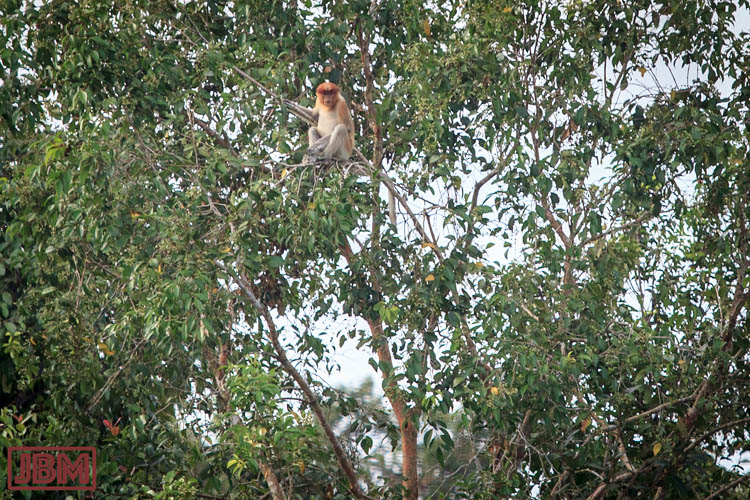
The Kebun Raya Balikpapan (Balikpapan Botanical Garden) is focussed on collecting, conserving and showcasing the unique trees, orchids and other plants of Kalimantan. Across its 307 hectares, it achieves this admirably. Most of that area consists of protected lowland dipterocarpus forest, which once blanketed much of the island of Borneo. This protected forest extends into the adjacent Hutan Lindung Sungai Wain (the Wain River Protected Forest), together forming a 10,000+ hectare window into the remarkable biodiversity of East Kalimantan.
Protection of the forest of course also protects the habitat of a huge range of other life: insects, reptiles, mammals, and… birds. So here’s a selection of just some of the birdlife I have recently encountered at the Kebun Raya. (For another selection, follow this link to view Part 2 of this post).
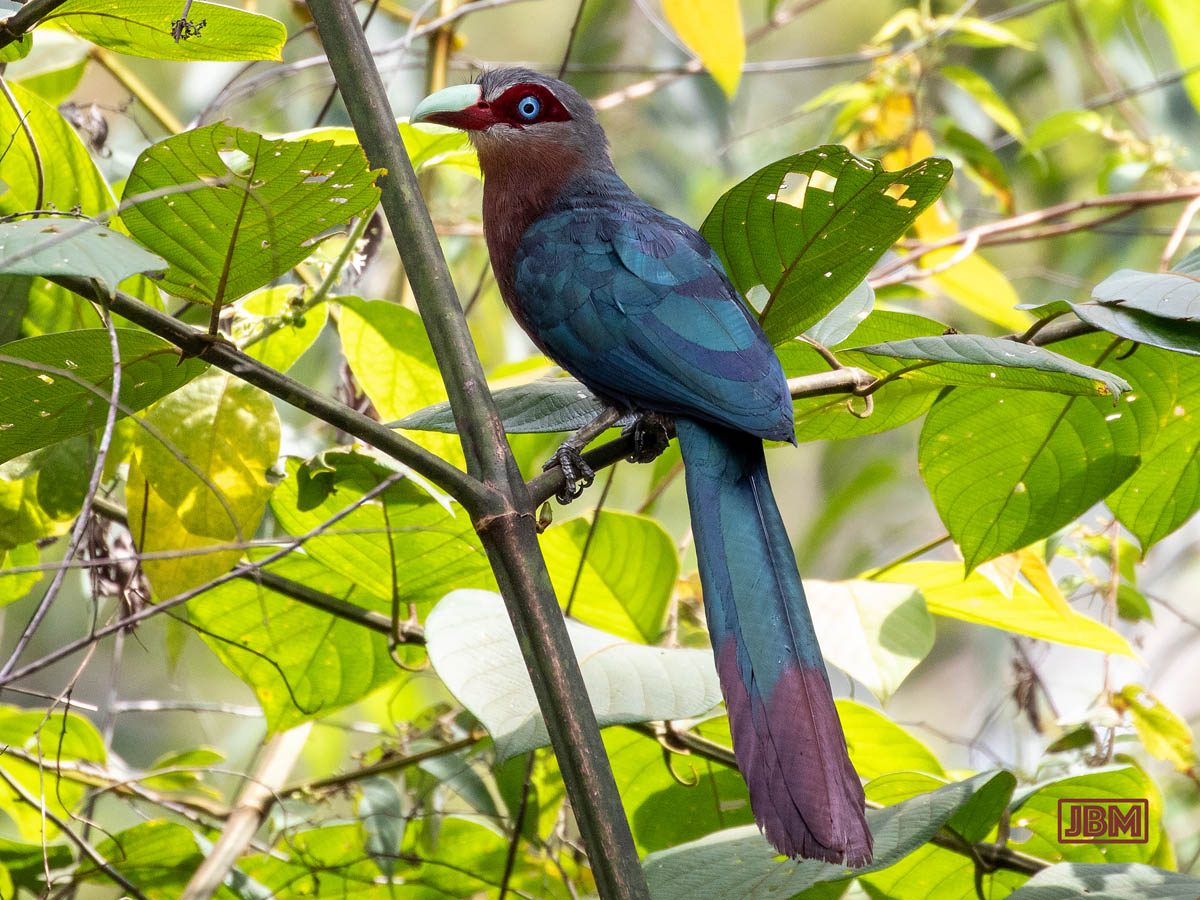
Chestnut-breasted malkoha (Phaenicophaeus curvirostris microrhinus)
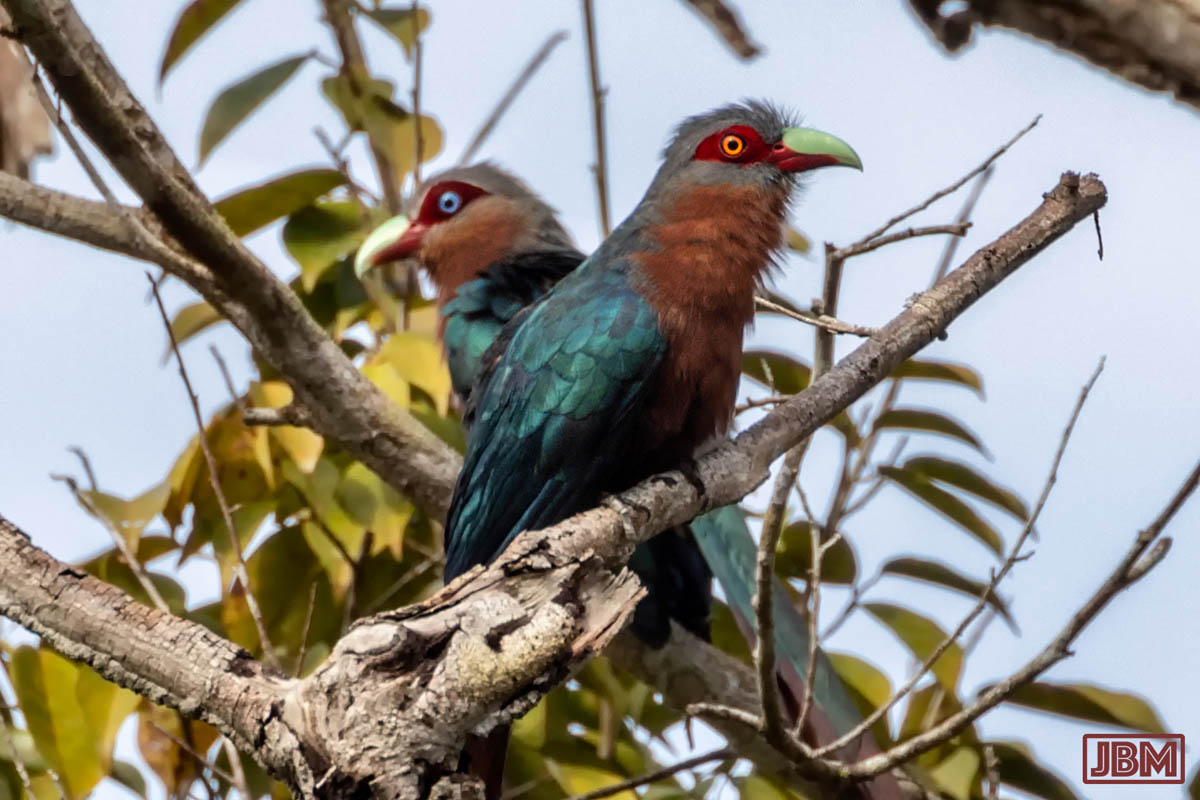

Apart from eye colour, the female (yellow iris) and male (blue) are almost indistinguishable.
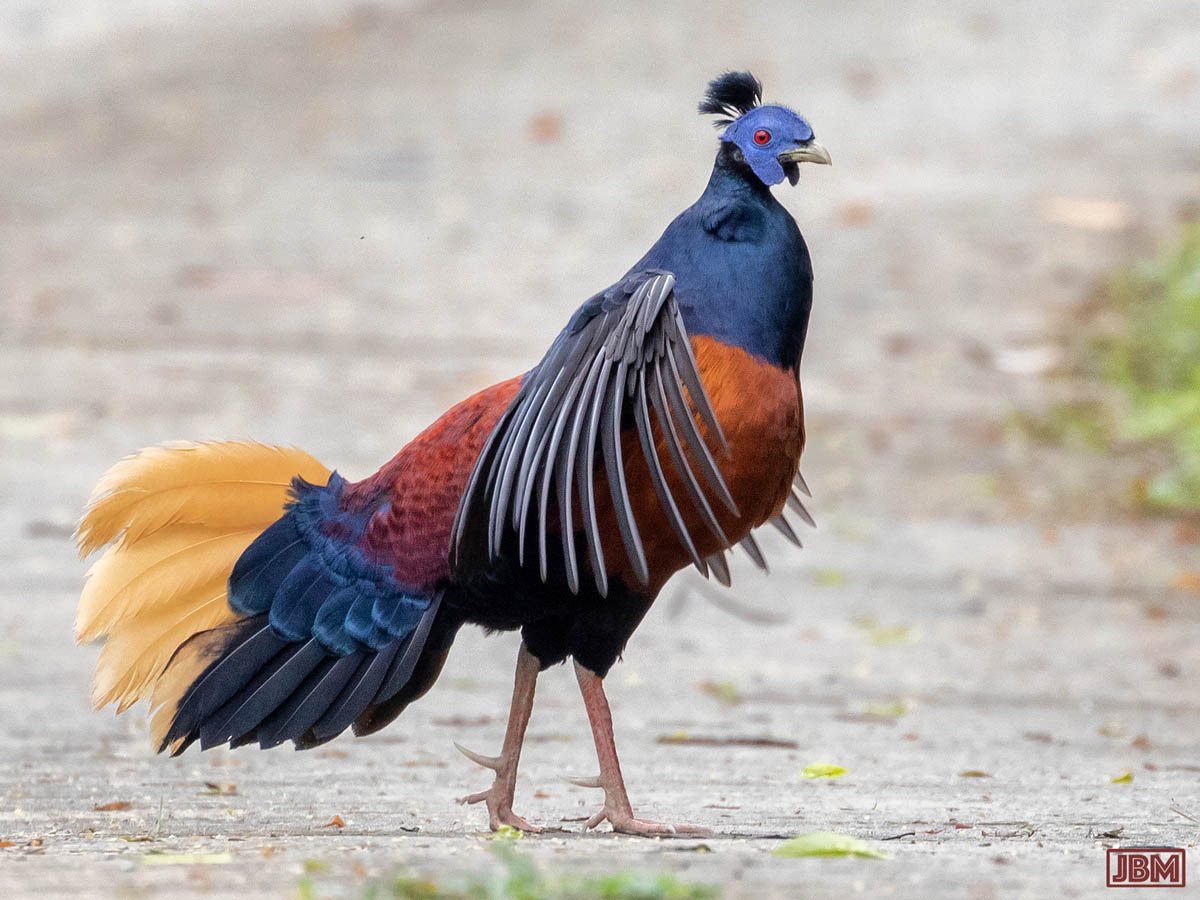
Bornean Crested Fireback (Lophura ignita in Latin, or ‘Ayam hutan’ locally)
This male was strutting proudly and showing off his fine plumage.
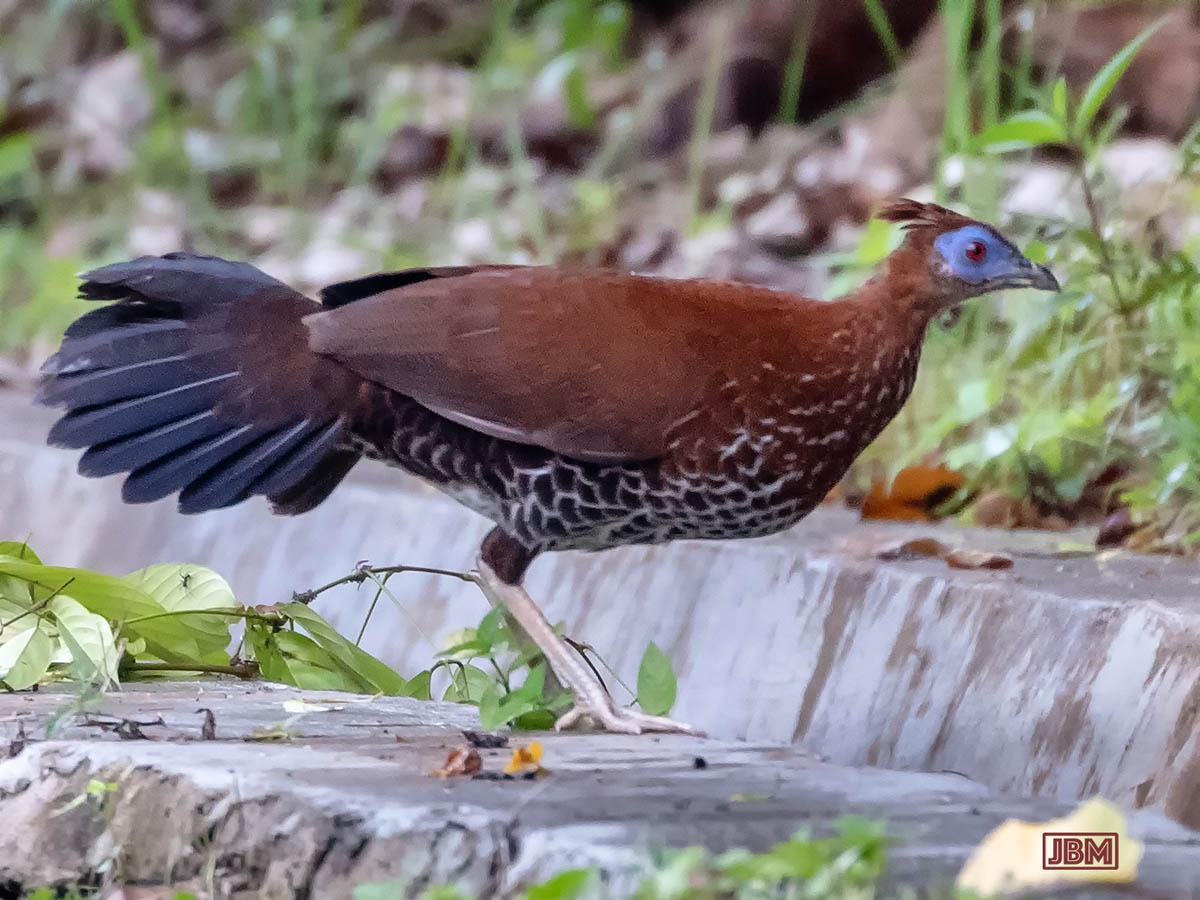
This female Bornean Crested Fireback is less dramatic and showy than its male partner – but no less beautiful.
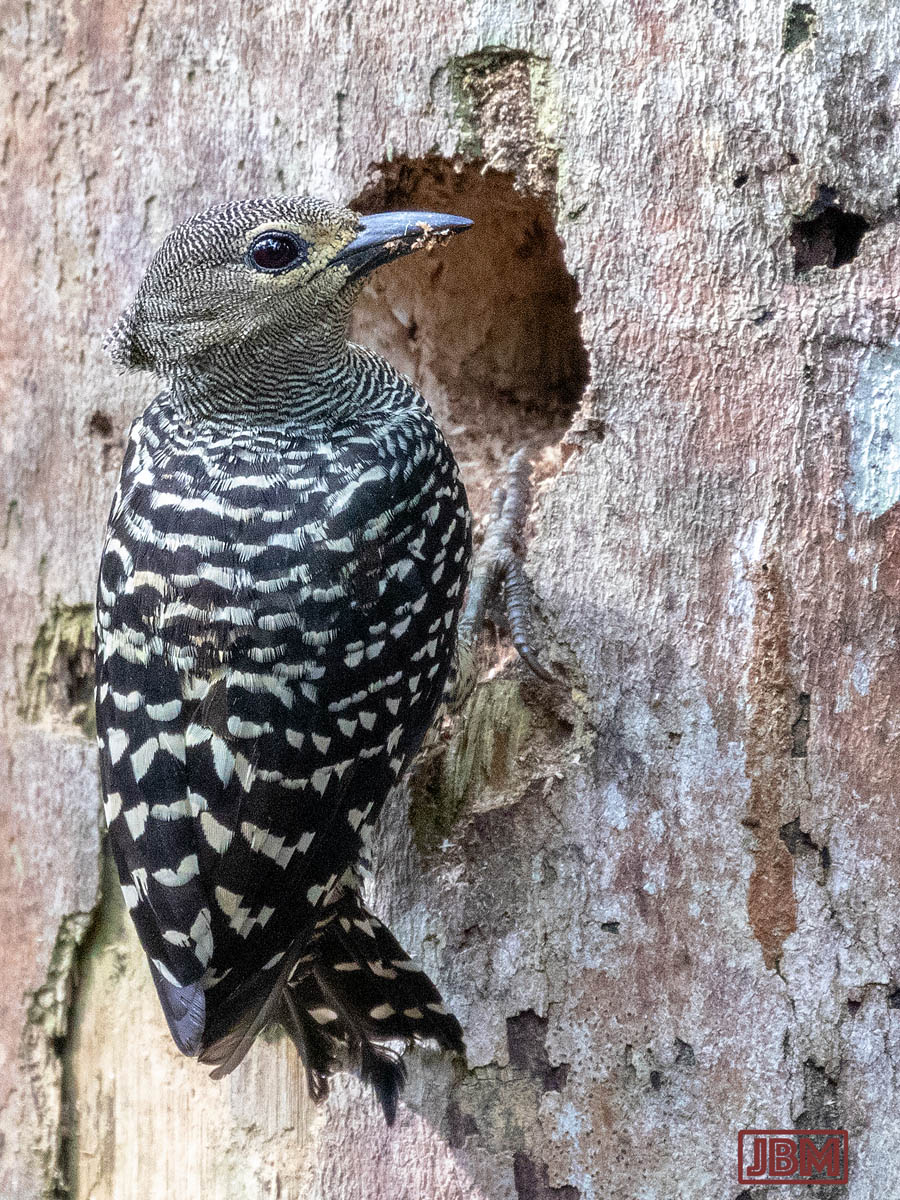
Buff-rumped woodpeckers (Meiglyptes grammithorax)
The male and female are almost identical, with the male distinguished by the red patch under his eye.
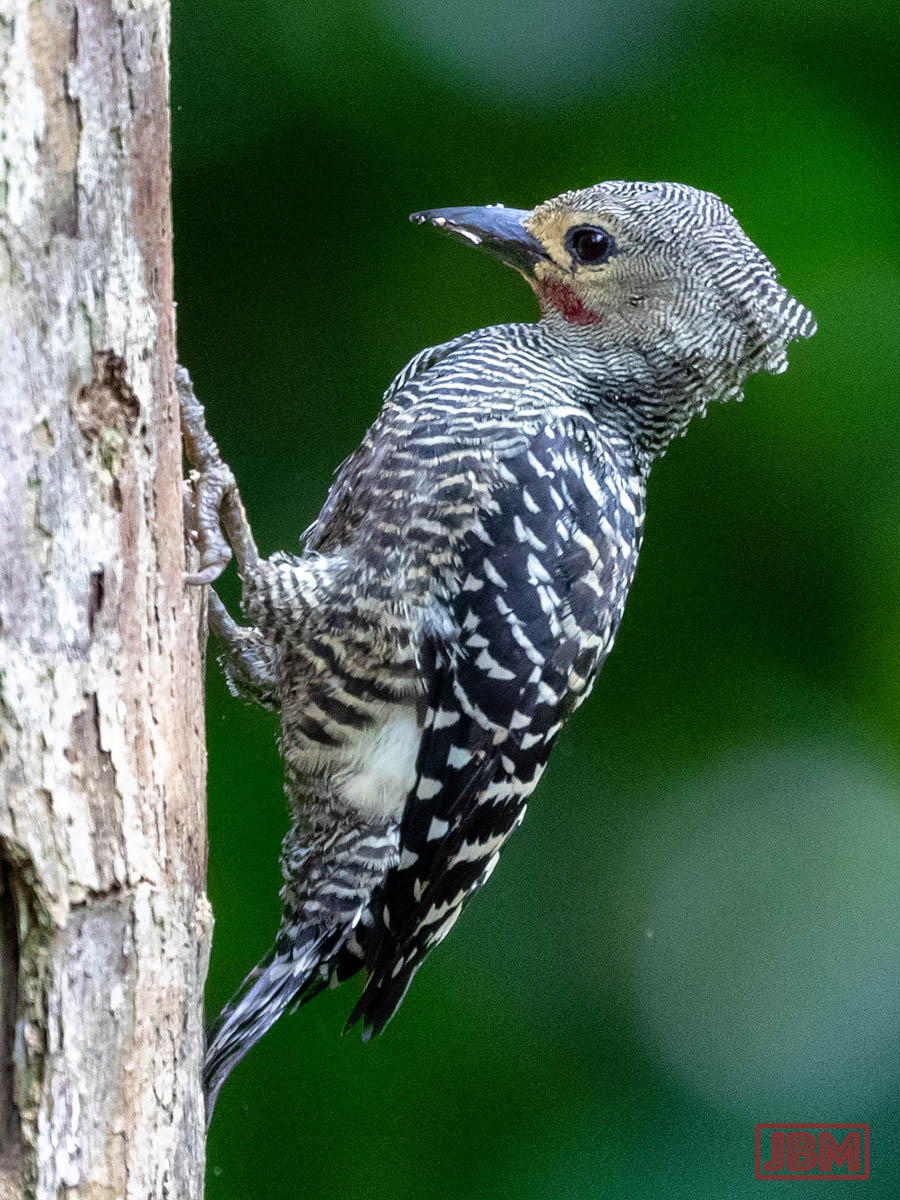

They were carving out quite deep holes in the trunk of a dead tree, in pursuit of termites. So engrossed were they in that task that they let me approach within about four metres.
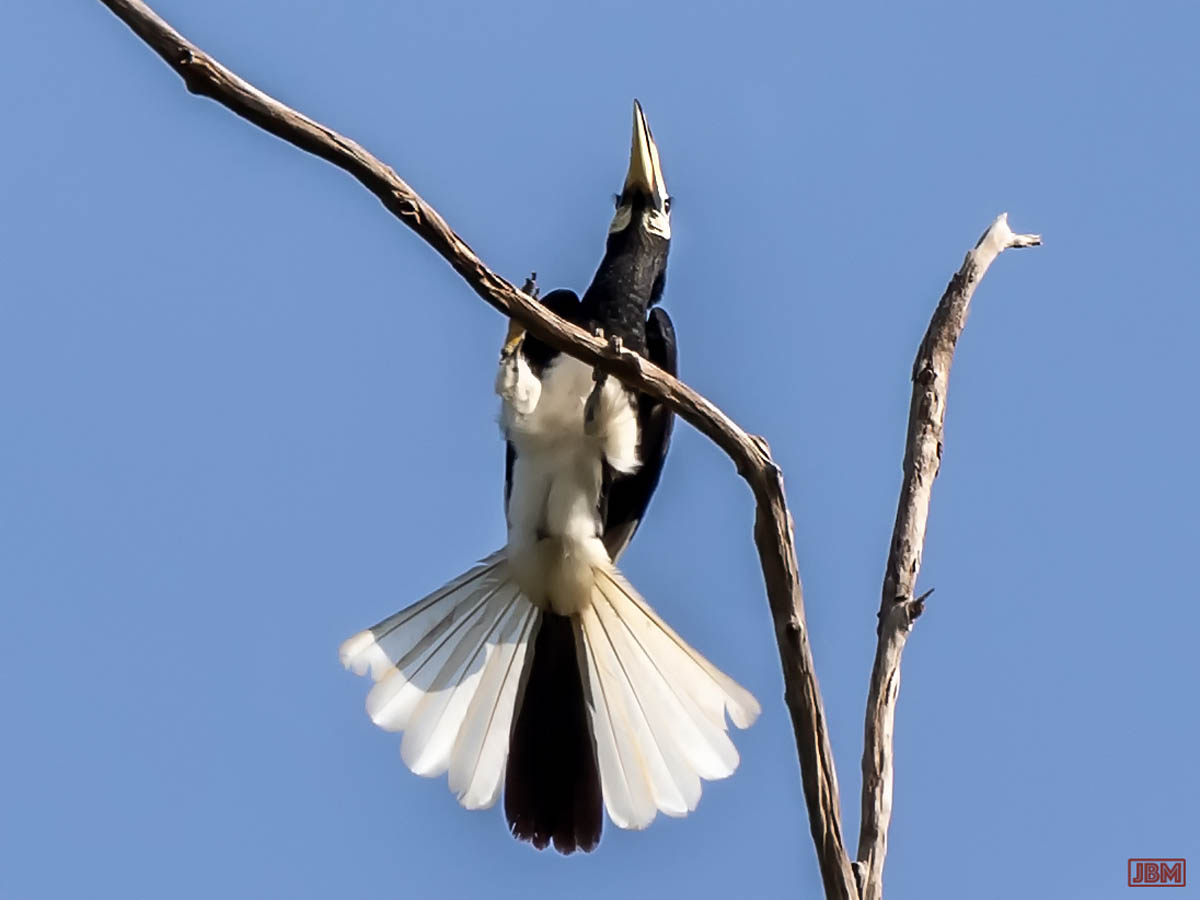
Pied oriental hornbill (Anthracoceros albirostris)
A wildlife photographer from Bandung (Java) visited the Kebun Raya Balikpapan recently, saying that he was very keen to see a hornbill bird while he was in Kalimantan. Not wanting to get his hopes up, I told him that they are often heard but quite rarely seen.
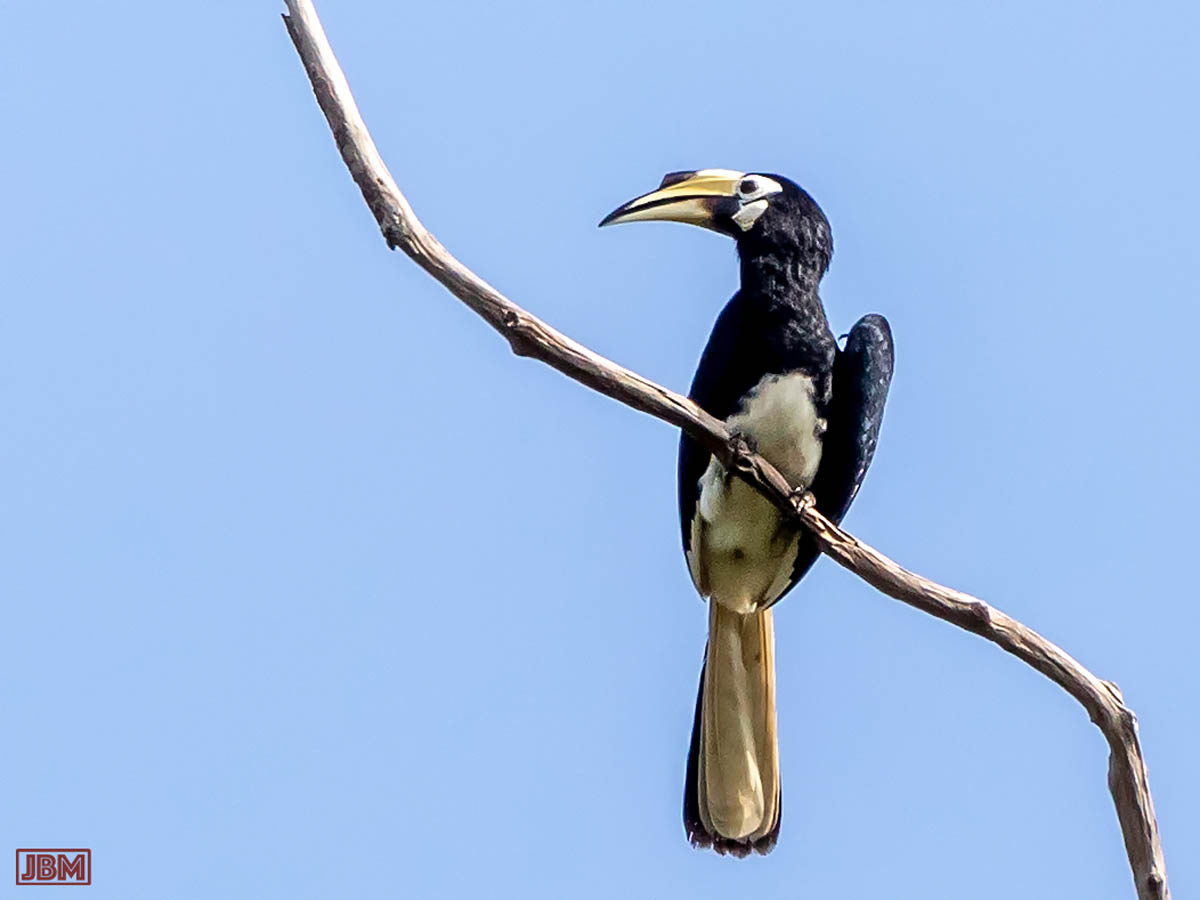

5 minutes later… this (female) Pied oriental hornbill.
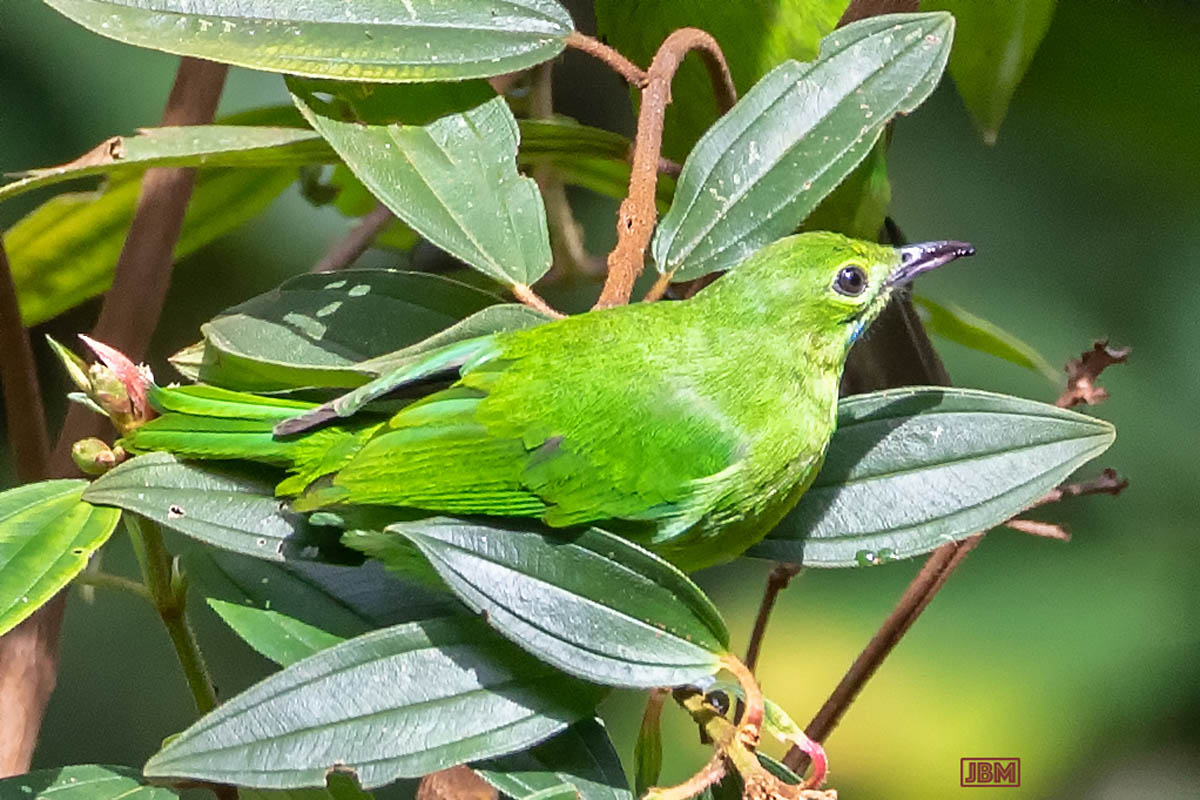
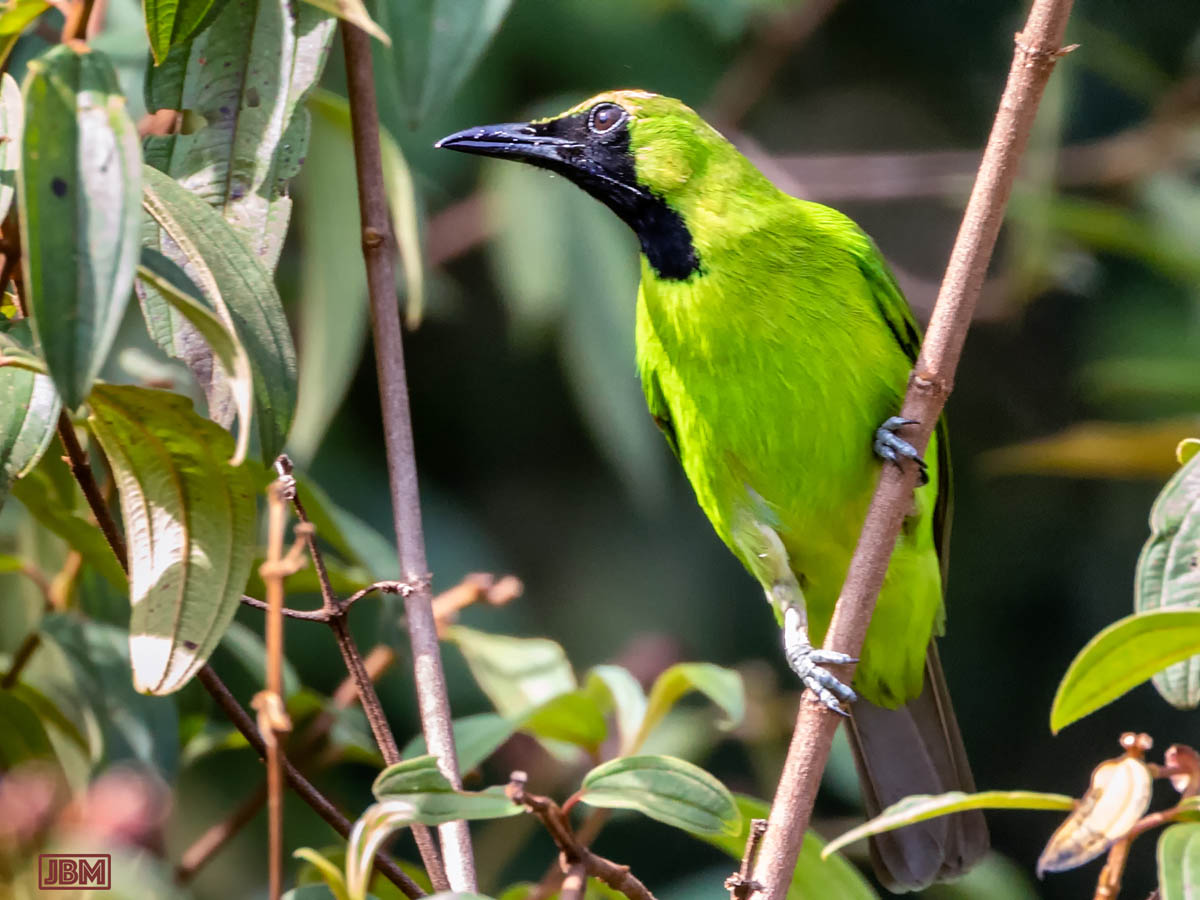
Lesser green leafbird (Chloropsis cyanopogon)
Like its close relative the Greater green leafbird (Chloropsis sonnerati), it is found in Indonesia, Malaysia, Thailand and Myanmar. The IUCN has determined that the survival of both species is threatened by habitat loss.
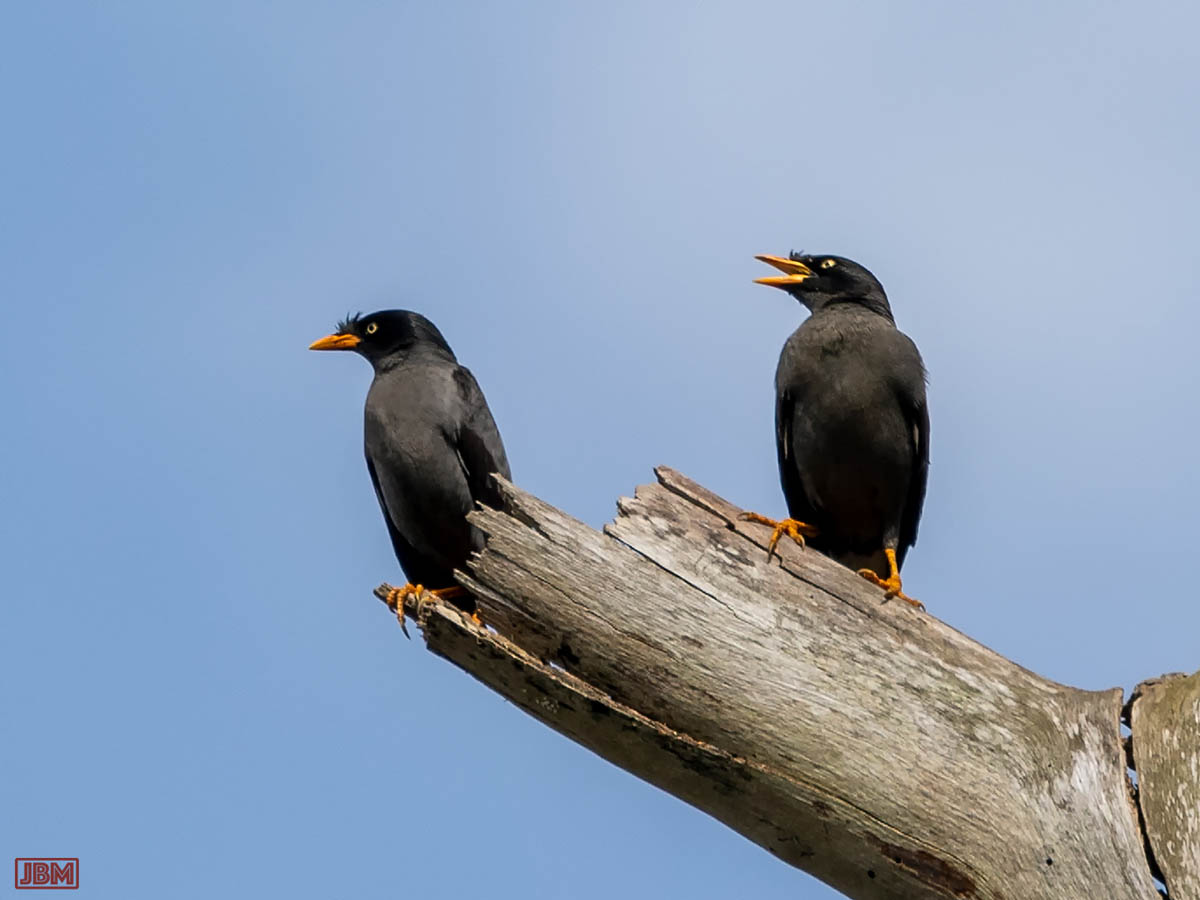
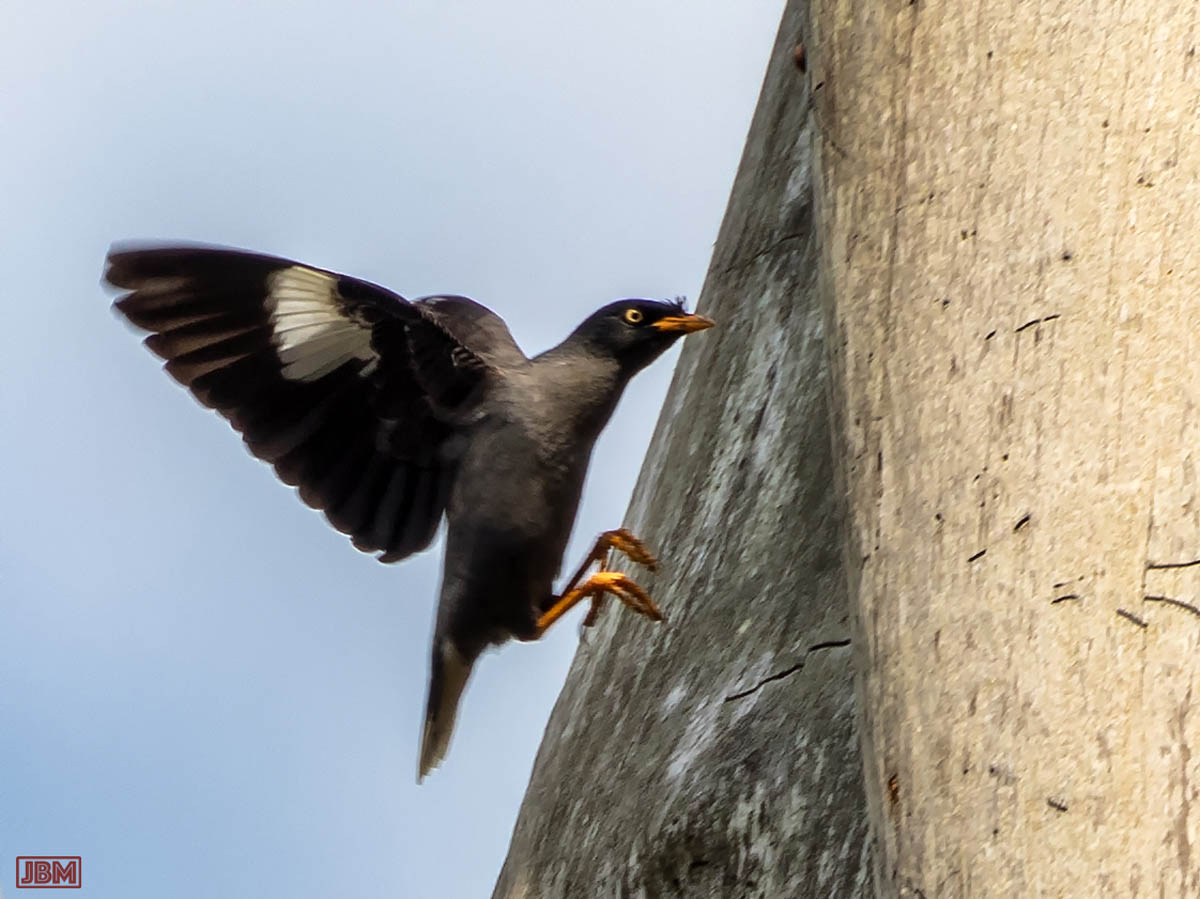
Javan myna (Acridotheres javanicus)
A member of the starling family, originally found only on Java and Bali, but has spread (or been introduced) to other islands and countries.
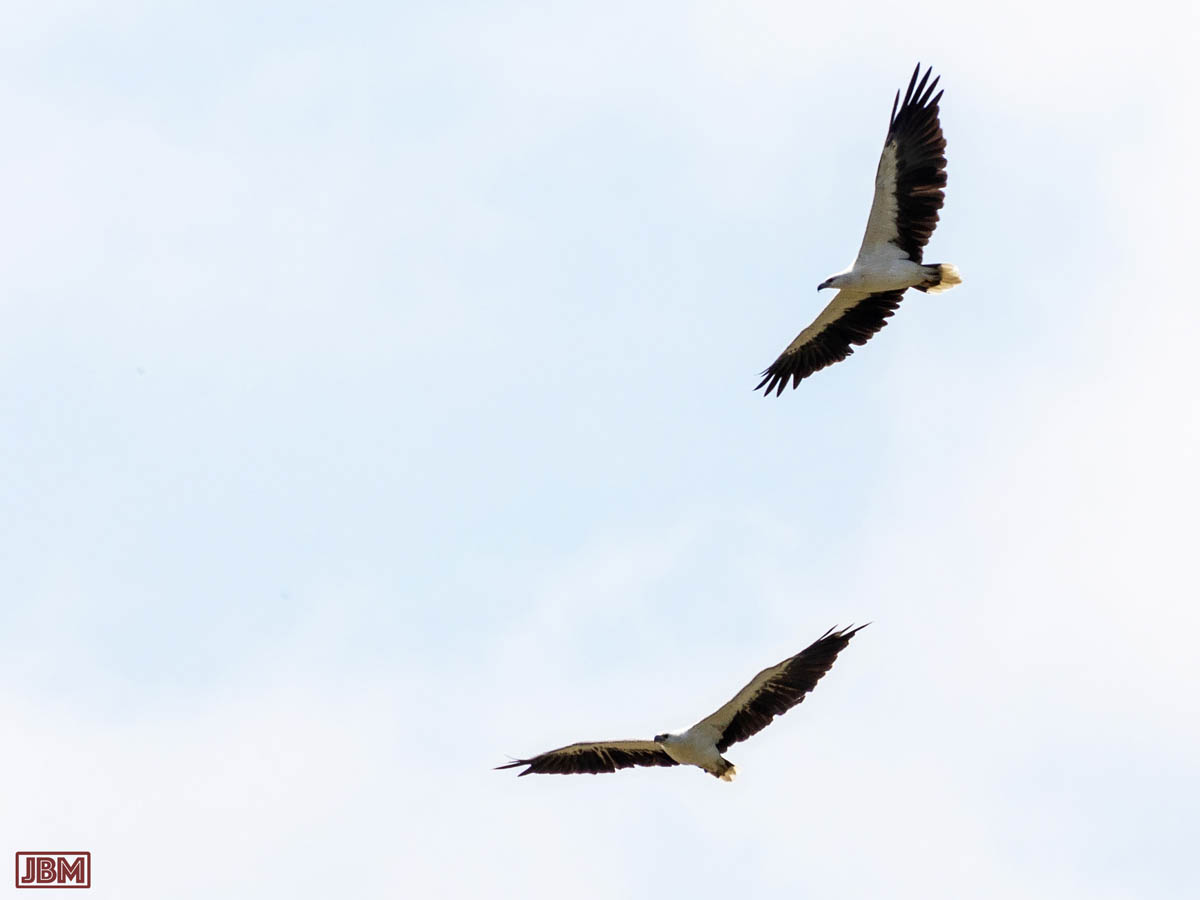
White-bellied sea eagles (Haliaeetus leucogaster)
They are found from western India to as far east as the Solomons and New Zealand (and Australia of course), but this was the first time I’ve seen them at the KRB…
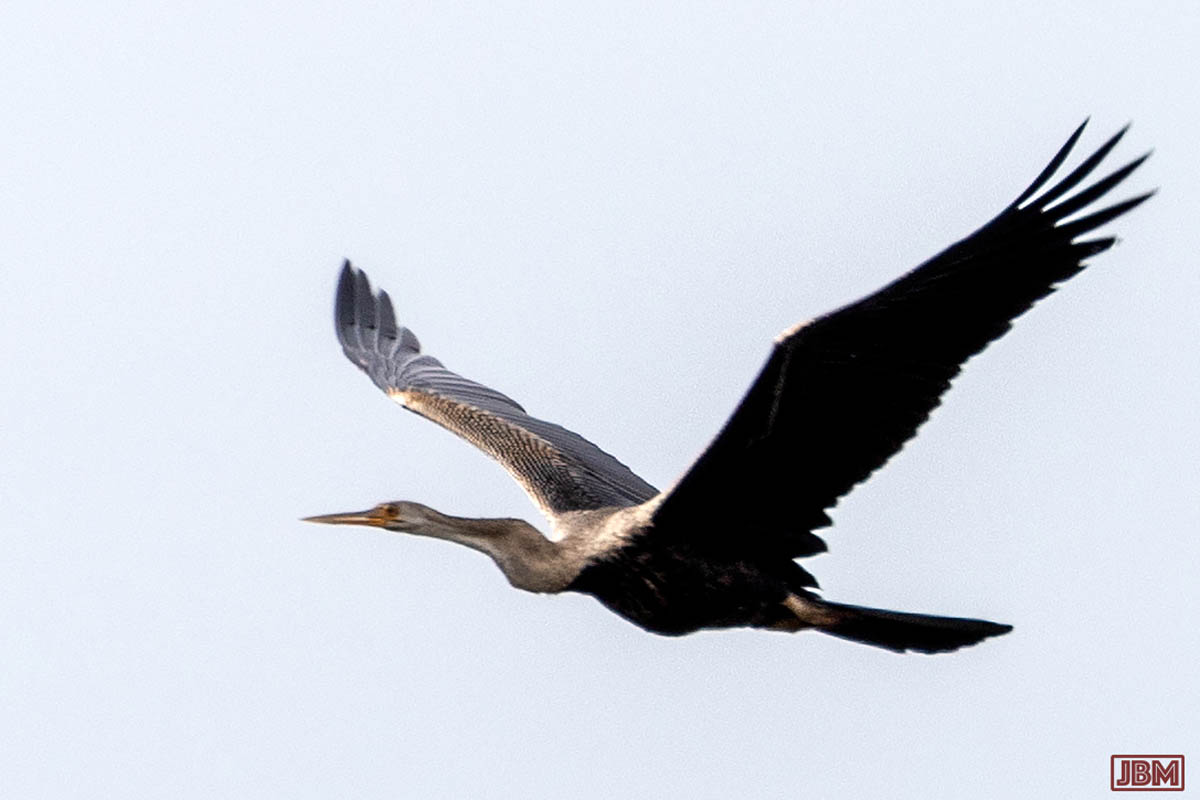
Oriental darter (Anhinga melanogaster)
They are also known as ‘snakebirds’, because only the very long neck and head is visible when the bird is immersed.
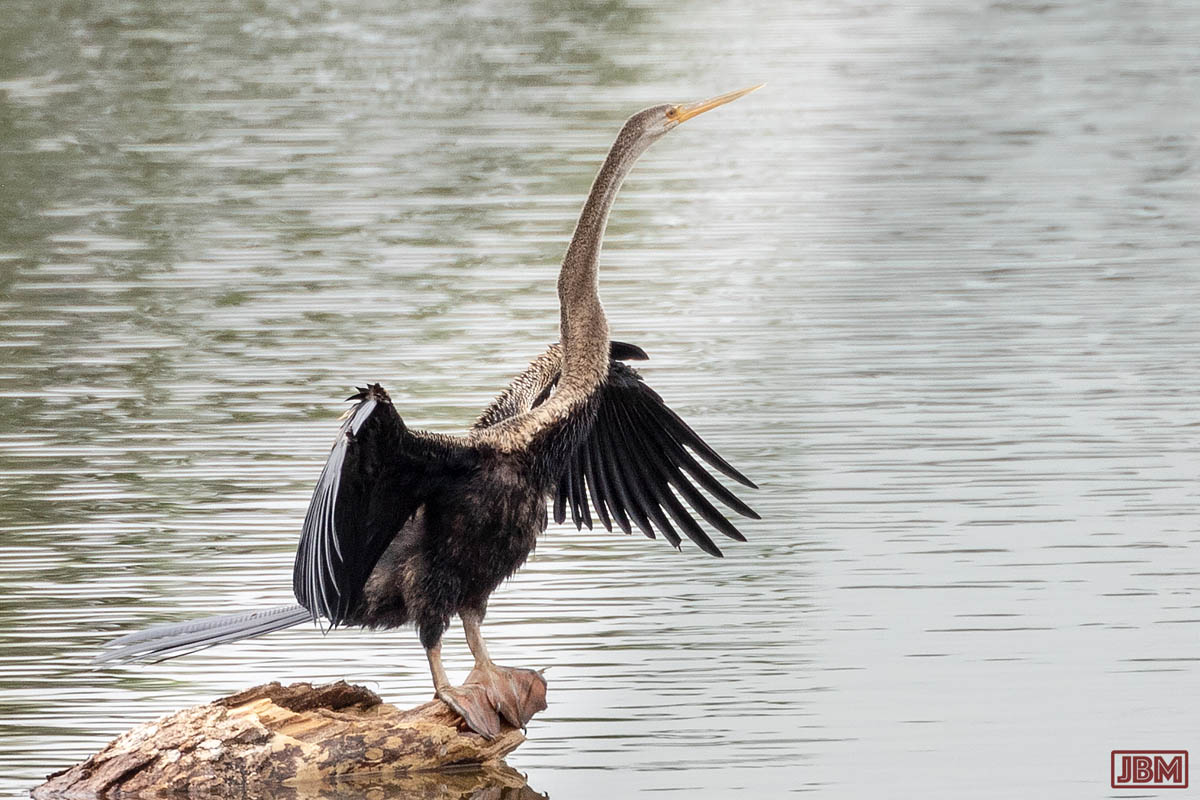

Like cormorants, they stand with their wings outstretched to dry them after swimming.
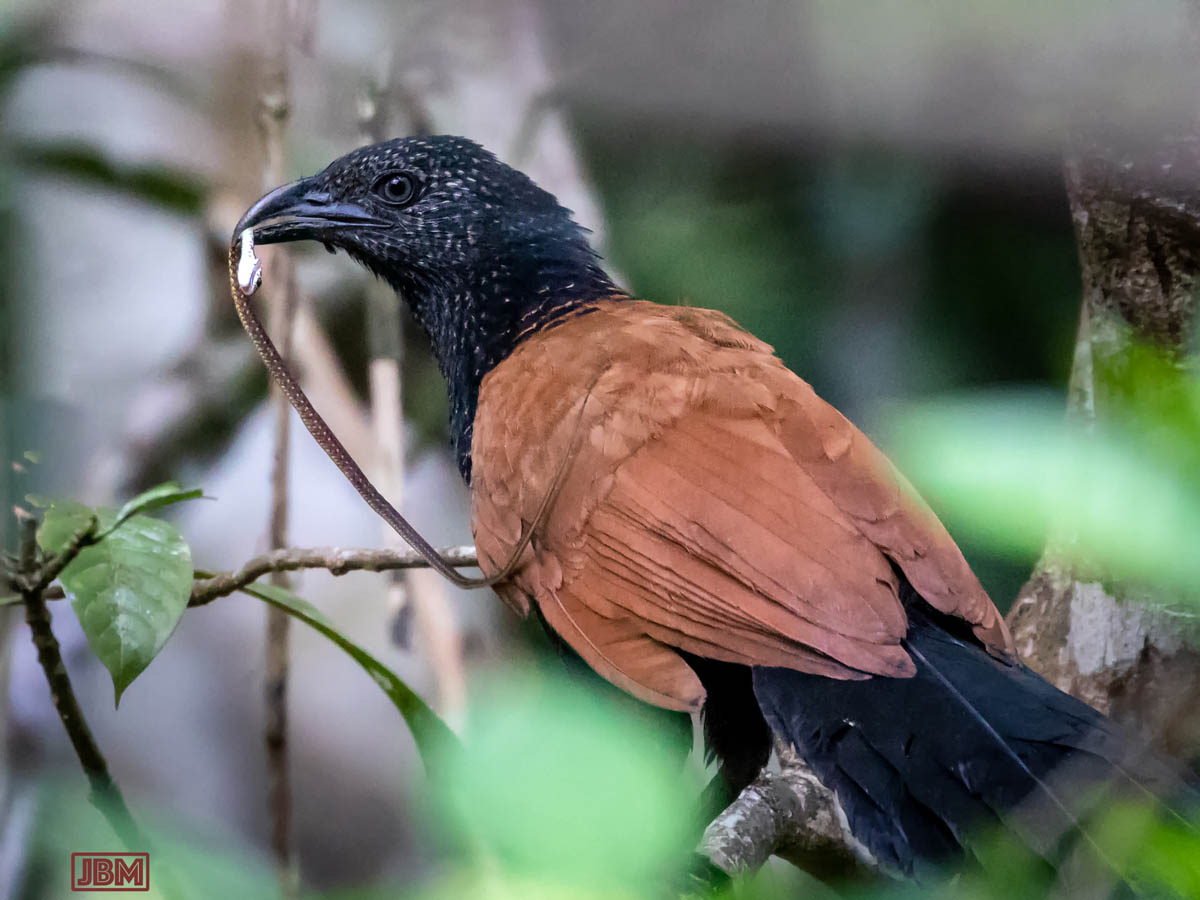
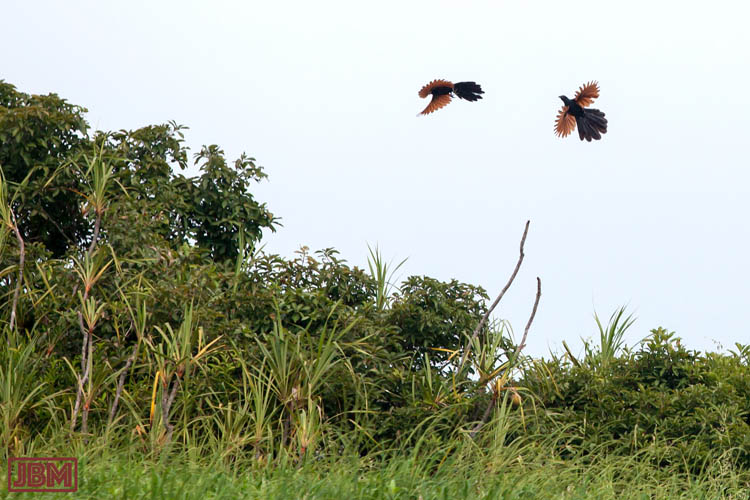
Greater coucal (Centropus sinensis bubutus)
I have seen ‘burung bubut’ before, in Central Kalimantan, but this was the first one I’d seen here in East Kalimantan.
I was even more delighted when I saw that it had just captured a little snake, which was hanging, still alive and wriggling, from its beak. (I was of course sorry for the hapless little snake, but… well, it’s a jungle out there).
The Greater coucal is a large species of (non-parasitic) cuckoo, found from western India and southern China down south as far as Java. They are reportedly becoming scarce in Kalimantan because local belief is that a medicine made from the bird’s wings is useful for healing broken bones.
Greater green leafbird (Chloropsis sonnerati)
These very attractive birds are well known in Indonesia as ‘Cucak hijau’. They have a lovely rich complex song, and are good mimics too. This one is a male.
This may lead to their extinction in the wild, because they are being heavily trapped and sold in bird markets for upwards of Rp1 million (about AU$100) each. Their owners may enter them in the birdsong competitions that are popular here. Betting and prize monies are big, and a competition winner can sell for many times the original purchase price.
20 years ago the IUCN classed them as of ‘Least concern’. But now, due to rapidly declining numbers and habitat loss, they are classed as ‘Vulnerable’.
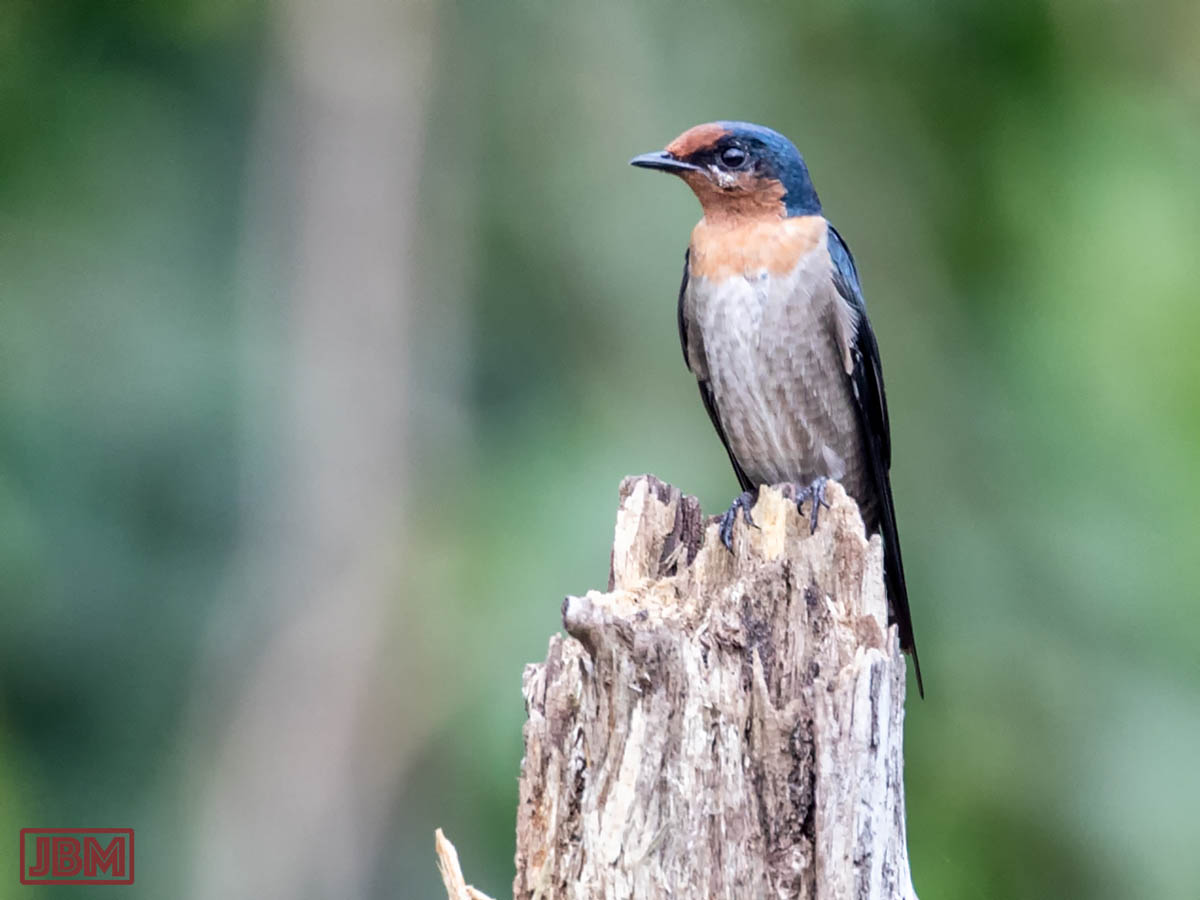
Pacific swallow (Hirundo tahitica)
It was perched atop a tall dead tree stump protruding from the middle of a pond. They are frequently seen across southern Asia and on the islands of the Pacific.